Menu
Key employment terms (KET) FAQ
Q: What is the purpose of the key employment terms (KET)?
A: The purpose of the key employment terms is to promote transparency & create trust between the employers & the employees. It is also designed to protect the employer so as to facilitate employment.
Q: What is the difference between an employment contract & key employment terms (KET) ?
A: They are different in terms of written style & clauses covered. An employment contract is usually written by a lawyer & it usually can be as lengthy as 10 to 15 pages. This is often designed for management staff & professionals, managers & executives (PMEs) earning more than S$4500 monthly.
As for key employment terms, it is usually prepared by a HR Manager & it is usually not longer than 1 page. Key employment terms are often prepared for rank & file employees & PMEs earning less than S$4500 monthly. All the key employment terms can be found in the MOM website.
A: They are different in terms of written style & clauses covered. An employment contract is usually written by a lawyer & it usually can be as lengthy as 10 to 15 pages. This is often designed for management staff & professionals, managers & executives (PMEs) earning more than S$4500 monthly.
As for key employment terms, it is usually prepared by a HR Manager & it is usually not longer than 1 page. Key employment terms are often prepared for rank & file employees & PMEs earning less than S$4500 monthly. All the key employment terms can be found in the MOM website.
Q3: Who is covered under the key employment terms (KET) ?
A: Professionals, managers & executives earning less than S$4500 monthly & all the rank & file employees covered under the Employment Act.
The Employment Act covers every employee (regardless of nationality) who is under a contract of service with an employer, except:
A: Professionals, managers & executives earning less than S$4500 monthly & all the rank & file employees covered under the Employment Act.
The Employment Act covers every employee (regardless of nationality) who is under a contract of service with an employer, except:
- Managers & executives who earn basic monthly salaries of more than S$4500,
- Seafarers,
- Domestic workers, &
- Statutory Board & government employees.
Q: Can the company change the key employment terms (KET) to other languages?
A: Yes, as long as all the information are there & they can be easily read & understood.
A: Yes, as long as all the information are there & they can be easily read & understood.
Q: In what format can the key employment (KET) terms be in?
A: If the company hires 3 or 4 employees, it can be in handwritten form. It can also be in soft or hard copy. Common key employment terms (e.g. leave policy that applies to a group of employees) can be provided in an employee handbook or company intranet.
A: If the company hires 3 or 4 employees, it can be in handwritten form. It can also be in soft or hard copy. Common key employment terms (e.g. leave policy that applies to a group of employees) can be provided in an employee handbook or company intranet.
Q: Who should the company issue the key employment terms (KET) to on/from 1st April 2016?
A: From 1st April 2016 onwards, Key employment terms must be issued to :-
A: From 1st April 2016 onwards, Key employment terms must be issued to :-
- Newly employed workers who start work on or after 1 April 2016,
- Workers who are covered by the Employment Act*, &
- Workers who are employed for a continuous period of 14 days or more.
Q: When should the company issue the key employment terms (KET) ?
A: Key employment terms must be issued within 14 days from the start of employment.
A: Key employment terms must be issued within 14 days from the start of employment.
Q: Key employment terms (KET) take effect from 1st April 2016. Employees hired from 1st April 2016 onwards need to be issued with the Key employment terms, what about those already working in the company?
A: It is optional for the company to issue the same Key employment terms to the existing employees. But as long as they leave their positions, the new employees replacing them have to be issued with the Key employment terms.
A: It is optional for the company to issue the same Key employment terms to the existing employees. But as long as they leave their positions, the new employees replacing them have to be issued with the Key employment terms.
Q: Owing to the job nature, workers have to work beyond 12 hours every day. So, the monthly Overtime hours may exceed 72 hours. What should the company do?
A: MOM is taking overtime very seriously. Employees are not allowed to work beyond 12 hours.
A: MOM is taking overtime very seriously. Employees are not allowed to work beyond 12 hours.
Q: If terms in the employment contract violate employment rights (i.e. Employment Act, CPF Act), does the contract still hold or will it be totally void?
A: If any of the employment terms is less favourable than the relevant provisions in the Employment Act and/or CPF Act, then the employment contract is illegal, null & void. The provisions in the two Acts will take precedence over any contractual term that is less favourable.
A: If any of the employment terms is less favourable than the relevant provisions in the Employment Act and/or CPF Act, then the employment contract is illegal, null & void. The provisions in the two Acts will take precedence over any contractual term that is less favourable.
Q: If the employee is serving probation, as the employer, the company asks the employee to work beyond their contractual working hours, do we need to pay overtime to them?
A: Yes, you need to. If the company requests their employees to work beyond their contractual working hours, the company has to pay overtime at the rate of at least 1.5 X the basic hourly pay. This is applicable regardless of the status of employment- probation, part-time, casual or temporary basis.
The contractual working hours (excluding break time) cannot exceed 8 hours in a day. For example, a part-time worker needs to work 4 hours a day. If he works exceeding 4 hours but less than 8 hours, then the compensation rate for his overtime is 1 X the basic hourly pay. If he works beyond 8 hours, the compensation rate for his overtime is 1.5 X his basic hourly pay. If he works on Sunday, the compensation rate for his overtime is 2 X his basic hourly pay.
The company cannot ask their employees to work beyond 12 hours, inclusive of overtime, per day. The overtime hours cannot exceed 72 hours per month. This is a very serious offence if the company violates it.
A: Yes, you need to. If the company requests their employees to work beyond their contractual working hours, the company has to pay overtime at the rate of at least 1.5 X the basic hourly pay. This is applicable regardless of the status of employment- probation, part-time, casual or temporary basis.
The contractual working hours (excluding break time) cannot exceed 8 hours in a day. For example, a part-time worker needs to work 4 hours a day. If he works exceeding 4 hours but less than 8 hours, then the compensation rate for his overtime is 1 X the basic hourly pay. If he works beyond 8 hours, the compensation rate for his overtime is 1.5 X his basic hourly pay. If he works on Sunday, the compensation rate for his overtime is 2 X his basic hourly pay.
The company cannot ask their employees to work beyond 12 hours, inclusive of overtime, per day. The overtime hours cannot exceed 72 hours per month. This is a very serious offence if the company violates it.
Q: If the employee cannot carry forward or en-cash their unutilised leave, can they complain to MOM?
A: The approval of an employee’s annual leave application is at the discretion of the employer. That means an employer can choose not to approve a leave application due to insufficient manpower or the application being made during peak periods. Nevertheless, employers should exercise flexibility when granting leave, taking into consideration the employee’s preference, & granting the applications whenever the situation permits.
A: The approval of an employee’s annual leave application is at the discretion of the employer. That means an employer can choose not to approve a leave application due to insufficient manpower or the application being made during peak periods. Nevertheless, employers should exercise flexibility when granting leave, taking into consideration the employee’s preference, & granting the applications whenever the situation permits.
Q: If an employee is serving probation, is the company supposed to give the employee any annual leave entitlement?
A: If the employee has worked for at least 3 months for the company (regardless of whether is he still on probation or confirmed), the company is to grant at least 7 days of paid annual leave. His entitlement increases with the number of years of service until it reaches the minimum of 14 days of paid annual leave. You may offer more paid annual leave than the minimum.
A: If the employee has worked for at least 3 months for the company (regardless of whether is he still on probation or confirmed), the company is to grant at least 7 days of paid annual leave. His entitlement increases with the number of years of service until it reaches the minimum of 14 days of paid annual leave. You may offer more paid annual leave than the minimum.
Q: Are employees serving probation entitled to medical claims?
A: If the employee has worked for at least 3 months, whether on probation or not, the employer is legally obliged to bear the medical examination fee, i.e. the medical consultation fee.
For other medical costs, such as medication, treatment or ward charges, the employer is obliged to bear such costs depending on the medical benefits provided for in the employee’s Employment Contract or the collective agreement signed between the company & the union.
A: If the employee has worked for at least 3 months, whether on probation or not, the employer is legally obliged to bear the medical examination fee, i.e. the medical consultation fee.
For other medical costs, such as medication, treatment or ward charges, the employer is obliged to bear such costs depending on the medical benefits provided for in the employee’s Employment Contract or the collective agreement signed between the company & the union.
Q: The employee is granted 2 rest days per month, & rest days are on a fixed weekday on alternate weeks, there is no replacement off-in-lieu if a rest day falls on a public holiday. Is this practice legal if this is written down in the employment contract?
A: Under the Employment Act, employees are entitled to one rest day each week without pay. The rest day can be Sunday or any other day of the week. For employees on shift duty, the rest day can be a continuous period of 30 hours if it is not possible to grant them one whole day off as a rest day.
If a rest day falls on a public holiday, then the next working day will be a replacement paid holiday.
A: Under the Employment Act, employees are entitled to one rest day each week without pay. The rest day can be Sunday or any other day of the week. For employees on shift duty, the rest day can be a continuous period of 30 hours if it is not possible to grant them one whole day off as a rest day.
If a rest day falls on a public holiday, then the next working day will be a replacement paid holiday.
Q: For an employee serving probation, does the company need to pay sick leave or medical benefits to the employee?
A: For a foreign employee, an employer is required to pay for sick leave or any medical benefits since from day 1 employment.
Local employees are entitled to paid sick leave & claim medical consultation fees only if they meet these qualifying conditions:
i) Have served the company for at least three months; &
ii) Have informed or attempted to inform you of their absence within 48 hours; &
iii) The sick leave is certified by the company's doctor or by a government doctor.
An employer also has the discretion to accept medical certificates from a private doctor or even a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) practitioner.
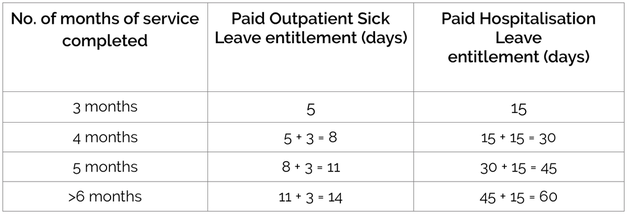
The number of days of paid sick leave employees are entitled to is given below:
A: For a foreign employee, an employer is required to pay for sick leave or any medical benefits since from day 1 employment.
Local employees are entitled to paid sick leave & claim medical consultation fees only if they meet these qualifying conditions:
i) Have served the company for at least three months; &
ii) Have informed or attempted to inform you of their absence within 48 hours; &
iii) The sick leave is certified by the company's doctor or by a government doctor.
An employer also has the discretion to accept medical certificates from a private doctor or even a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) practitioner.
The number of days of paid sick leave employees are entitled to is given below:
Q: If the company requests employees to work on rest days, how should the company compensate them?
A: Employers cannot force employees to work on a rest day unless under exceptional circumstances, such as when the nature of work requires it to be carried on continuously across successive shifts. Employees' agreement must be sought for this arrangement.
Under the Employment Act, the amount payable depends on the work duration & whether the request originated from the employee or employer.
A: Employers cannot force employees to work on a rest day unless under exceptional circumstances, such as when the nature of work requires it to be carried on continuously across successive shifts. Employees' agreement must be sought for this arrangement.
Under the Employment Act, the amount payable depends on the work duration & whether the request originated from the employee or employer.
Q: If the company asks a part-time employee to work on a public holiday, what is the correct way to pay him?
A: An employee is considered as a part-time employee if their contractual working hours is less than 35 hours per week. Under the law, employers are allowed to pro-rate the employment benefits of a part-time employee to that of a full-time employee according to the hours worked. The employee's public holiday entitlement is pro-rated based on the number of hours worked as compared to a full-time employee.
The formula to compute the public holiday entitlement for a part-time employee is =
A: An employee is considered as a part-time employee if their contractual working hours is less than 35 hours per week. Under the law, employers are allowed to pro-rate the employment benefits of a part-time employee to that of a full-time employee according to the hours worked. The employee's public holiday entitlement is pro-rated based on the number of hours worked as compared to a full-time employee.
The formula to compute the public holiday entitlement for a part-time employee is =
A part-time employee is entitled to the pro-rated public holiday payment regardless of whether it falls on his working or non-working day. If the employee works on a public holiday, he would be paid for the hours worked in addition to the holiday pay.
Q: If a part-time employee earns less than $500/month & requests the company not to contribute CPF, to instead pay him the CPF in cash instead, can the company allow this?
A: Under the CPF Act, CPF is payable for all Singapore citizens & Singapore ermanent residents. This is applicable even if they are working on part-time/ ad-hoc/ contract basis & during probation.
If employees earn less than $500 per month, they do not have to contribute the employee share of the CPF. CPF contributions are borne solely by the employer.
A: Under the CPF Act, CPF is payable for all Singapore citizens & Singapore ermanent residents. This is applicable even if they are working on part-time/ ad-hoc/ contract basis & during probation.
If employees earn less than $500 per month, they do not have to contribute the employee share of the CPF. CPF contributions are borne solely by the employer.
Q: Can CPF be paid only on an employee’s basic salary, & not on commissions & allowances?
A: Besides the basic salary, CPF contribution is also payable for commissions; allowances like Per Diem allowances & housing allowances; cash incentives/awards like Chinese New Year Ang Bao & overtime pay & bonuses.
A: Besides the basic salary, CPF contribution is also payable for commissions; allowances like Per Diem allowances & housing allowances; cash incentives/awards like Chinese New Year Ang Bao & overtime pay & bonuses.
Q: If the employer helps the employee to pay for the monthly accommodation directly to his landlord, does the company still need to pay CPF on this so-called housing allowance?
A: CPF contribution is payable if the housing allowance is paid to the employee. However, no CPF contribution is payable if it is paid directly to his landlord.
A: CPF contribution is payable if the housing allowance is paid to the employee. However, no CPF contribution is payable if it is paid directly to his landlord.
Q: If an employee is not aware of the notice period for resignation, & fails to serve the resignation notice, can the company deduct the employee’s salary, or demand compensation for the notice period ?
A: Under the Employment Act, either party to an employment contract could terminate the contract by serving the appropriate notice or by paying salary in lieu of notice to the other party.
The notice period shall be in accordance with what is spelt out in the contract of service or mutually agreed between the two parties.
If the employee fails to serve the appropriate notice, the employer can deduct the employee’s salary or demand compensation for the shortfall in the notice period.
The term pertaining to monetary compensation for premature termination of the contract is a private contractual agreement & is not governed by the Employment Act.
The Civil Court will have jurisdiction in deciding such disputes. Both parties may wish to consult their lawyers on this matter.
A: Under the Employment Act, either party to an employment contract could terminate the contract by serving the appropriate notice or by paying salary in lieu of notice to the other party.
The notice period shall be in accordance with what is spelt out in the contract of service or mutually agreed between the two parties.
If the employee fails to serve the appropriate notice, the employer can deduct the employee’s salary or demand compensation for the shortfall in the notice period.
The term pertaining to monetary compensation for premature termination of the contract is a private contractual agreement & is not governed by the Employment Act.
The Civil Court will have jurisdiction in deciding such disputes. Both parties may wish to consult their lawyers on this matter.
Q: If the employee did not sign an employment contract, can I deduct or withhold the employee’s salary & demand for compensation if the employee resigns without serving notice?
A: A Contract of Service may be written or oral. If the employee fails to serve the appropriate notice in accordance with what is spelt out in the contract of service or mutually agreed between the two parties, the employer can deduct the employee’s salary or demand compensation for the shortfall in the notice period.
A: A Contract of Service may be written or oral. If the employee fails to serve the appropriate notice in accordance with what is spelt out in the contract of service or mutually agreed between the two parties, the employer can deduct the employee’s salary or demand compensation for the shortfall in the notice period.
Q: Is it mandatory or compulsory for employers to give employees the annual wage supplement (AWS) i.e. 13th month?
A: AWS (commonly known as the 13th month payment) is not a compulsory payment under the Employment Act. AWS payment is subject to negotiation & mutual agreement between the employer & the employee.
A: AWS (commonly known as the 13th month payment) is not a compulsory payment under the Employment Act. AWS payment is subject to negotiation & mutual agreement between the employer & the employee.
Q: Can the company ask the employee to start work before he signs the employment contract? Is it illegal ?
A: It is not illegal to start work without an employment contract. However, to avoid any misunderstanding, it is advisable for employers to give a written Employment Contract or Appointment Letter that states the terms & conditions of employment.
The employment contract should include:
A: It is not illegal to start work without an employment contract. However, to avoid any misunderstanding, it is advisable for employers to give a written Employment Contract or Appointment Letter that states the terms & conditions of employment.
The employment contract should include:
- Title of job,
- Scope of work,
- Start date of appointment for work,
- Salary & allowances if any,
- Salary payment period,
- CPF contributions,
- Hours of work per day/ week/ shift patterns,
- Rate of overtime payment,
- Rest day,
- Employee’s benefits eg. annual leave, sick leave & hospitalisation leave,
- Termination of employment contract & notice period.
Q: Can the employer change the terms in the employment contract after it is signed? Or would both parties’ consent be required for any amendment?
A: Both the employer & employee are bound by the contract of service that was signed at the beginning of employment. This contract should not be amended or changed without the consent of both parties concerned.
If the employer would like to amend the terms & conditions of employment as stated in the employment contract, it would need to negotiate with the affected employees or their union.
Employees who do not agree to the changes should raise their objections directly to the employer for negotiation. Ultimately, if there is no agreement reached on the changes to the employment contract, either party could choose to terminate the contract of service by giving the appropriate notice or payment in-lieu of notice.
Otherwise, employees could be deemed to have accepted the revised terms of employment.
A: Both the employer & employee are bound by the contract of service that was signed at the beginning of employment. This contract should not be amended or changed without the consent of both parties concerned.
If the employer would like to amend the terms & conditions of employment as stated in the employment contract, it would need to negotiate with the affected employees or their union.
Employees who do not agree to the changes should raise their objections directly to the employer for negotiation. Ultimately, if there is no agreement reached on the changes to the employment contract, either party could choose to terminate the contract of service by giving the appropriate notice or payment in-lieu of notice.
Otherwise, employees could be deemed to have accepted the revised terms of employment.
Location |
|